
TITLE
BRAKED MULTI-PURPOSE AEROSTATIC PLATFORM, WHICH CAN BE LIFTED TO VARIABLE HEIGHTS, PRIMARILY DESIGNED TO SUPPORT ANTENNA SYSTEMS FOR RADIO TRANSMISSION OF VOICE AND DATA. MULTIPLE DEVICES CAN ALSO BE INSTALLED ON BOARD, SUCH AS AERIAL SURVEY DEVICES.
PATENT NUMBER
This new and innovative system of aerostatic platforms, referred to as ZM-08, which has been adapted to contain gas (helium or hydrogen) in order to rise to varying heights according to the principle of Archimedes, lends itself to a wide variety of applications and thus allows for the performance of several functions in every part of the world. The invention was primarily created, to transport antenna systems to a sufficient height for the radio transmission of voice and data and to achieve a greater coverage of the land area.
On these aerostats, it is also possible to install multiple display and aerial detection devices, such as:
- Stylus Antennas
- Dipole Antennas
- Cameras capable of take 360° shots
- Motorized Cameras (Photo)
- Thermal Imagers
- Laser
- Instruments for monitoring air pollution
- Systems for the detection of meteorological data
- Motorized spotlights
- Test devices
INNOVATION
The main factors that make this system innovative are the following:
1 - The ability to support antennae or other equipment on the north pole of the aerostat correctly, without compromising the stability of the platform.
2 - The possibility of simultaneously using the top and bottom parts of the aircraft.
3 - Its extreme versatility allows the use of many devices on the operating field. This is all thanks to the specially designed supports that facilitate its ability to adapt effectively to the multiple devices that can be placed on board.
4 - Speed and simplicity of the operating processes for the installation or replacement of equipment. By virtue of this ability, different devices can be used during the course of the same day.
5 - Customisability, which allows you to configure the platform as needed. It allows you to remove and replace the entire support with another one of a different shape and size. Also, you can decide whether to implant and use the support on the upper part, the lower part, or on both poles where necessary.
DESCRIPTION
This aerostat, preferably with an aerodynamic shape to offer less resistance to wind flow, is equipped with a central and vertical through-hole, open at its upper and lower ends, to secure and support the antenna or other equipment with various types of support, using suitably lightweight materials. These support devices will be installed by force or via interlocking with a snap lock, using short, shaped sections, which are connected to the aerostat by welding, gluing, etc.
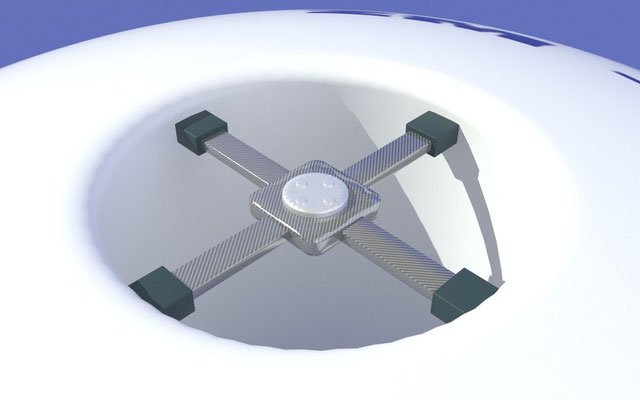


The aforementioned antenna can be connected with a vertical coaxial cable, the lower end of which is connected with one or more devices for the radio transmission of voice and data. The lifting and lowering of the system occurs via a safety rope, unwound and rewound using a winch. The winch can be manual or electric (the latter preferably operated with a radio remote control to prevent the operator from being under the structure during manoeuvres, thereby ensuring safety). The platform is further anchored to the ground by mooring ropes, provided in sufficient quantity to ensure that the aerostat is properly attached to the ground. These braces are attached to the hooks, which are fixed along the centre line of the outer wall of the aerostatic globe, and spaced evenly. The mooring lines are progressively dragged up towards the top of the platform during lifting. In case of special need, the ZM-08 can also be used without the anchoring tie rods, and operated with only the central rope.
To increase security, the lower part of the system can be equipped with light and sound indicators which indicate its ascent and descent, while the upper part can be equipped with aircraft warning lights. This can all be powered by adhesive solar panels.
The aerostat is equipped with valves for the inflation and deflation of the housing. The valves are also able to guarantee efficient gas recovery. Furthermore a safety valve is provided which can expel any gaseous substance present in excessive quantities caused by the volumetric increase of the internal chamber. This phenomenon is due to variations in atmospheric pressure or temperature.
Size and Load
The increase of the useful load on board determines the dimensions of the aerostat, the volume of which must be directly proportional to the increase of the weight to be supported. The ZM-08, therefore, will be designed according to its areas of application, with appropriate shapes and sizes. The system, in fact, can be produced with overall dimensions of a few metres, ranging up to the production of aerostats with a size of tens of metres.
It should be noted that to keep the platform, together with the device supports and the components connected to it, anchored to the ground and to allow lifting, lowering, and so on, it is preferable that everything be made with the lightest possible materials, thereby decreasing the amount of helium or hydrogen needed to lift it, and consequently reducing the space requirements of the system.
Operational height and anchoring Systems
Depending on its usage, the operational height and the method for mooring the aircraft to the ground may vary.
The balloon can be braked with a central rope, with the addition of lateral bracing or the single safety rope.
Below are two examples of use:
Use with lateral anchors
System suitable for radio transmissions, video monitoring, etc. In this case, the optimum operating height (especially for the amateur radio sector) would be about 50 metres, but this does not exclude the possibility of raising it higher, while taking into consideration that the distance between the ground anchor points with respect to the centre increases with increasing altitude.
In the demo video, four moorings appear. This number is only meant as an example, not a limit. The upper ends of these ropes may be attached to the platform using two methods:
1° - Fasten them to the corresponding hooks, affixed (welded, glued, etc.) directly to the outer peripheral surface.
2° - Connect to the traditional net. Depending on the type of use, the latter, although adding to the balloon’s load, offers in many cases the advantage of ensuring greater security for the system. It increases resistance to wind flow, preventing potential damage to the casing, since the coupling points are not affixed directly to the outer wall of the platform, as in the first method.


The lower end of each rope can be anchored to the ground using various systems. Here are a few examples:
- Picket metal with a hoop or curved hook
- Coil with belt tensioners (fixed to the ground with tent pegs, bolts, etc.)
- Buoys (in the case of use in water)
- Concrete dead weight
- Ballasts fillable with water, sand, soil, etc., e.g.
- Rigid plastic, fiberglass, or metal container
- PVC, jute, raffia bag
- Hesco Bastion
Use with only one central safety rope
With this method, the ZM-08 can raise its antennas at higher heights than the previous configuration, taking into account of course that due to the lack of lateral bracing, the platform will have less resistance to hostile weather conditions. This system is particularly useful also for weather reporting, monitoring of air pollutants and other aerial surveys.
Life at high altitude
In optimal conditions, the aerostat can remain in the air for a long time, provided gas refills are carried out periodically. The flight can also be momentarily interrupted for the following reasons: severe weather conditions, replacement of equipment, change of configuration backups, inspections, maintenance, various repairs, etc.
Materials
Casing
It will be made of an elastomeric material. In case of specific needs, the platform may be made with a rigid casing.
According to the materials on the market today, the system can be manufactured, for example, with the classic double casing:
1° - Chamber, adapted to contain the gas (which will provide the lifting force for the aircraft), made of Thermoplastic Polymers (polyurethane).
2° - Outer covering in Nylon Rip-Stop, which serves to protect the internal parts against weathering and ultraviolet rays. Moreover, this second layer allows the coupling of the anchoring ropes and other accessories, avoiding stress on the inner structure, which will be limited almost exclusively to containing the aeriform substance, considerably reducing the risk of possible damage.
Supports
These will be built with light and resistant materials. Carbon fibre, glass fibre, aluminium, etc.
Mooring ropes
The aforementioned means of anchoring are made of a suitably flexible and robust material, for example in the form of woven textile fibres.
Central safety rope
Made with the same materials as the above mooring lines. In some types of aerostats, the material used for such rope can be formed from woven steel wires.
Short shaped sections
Made of rubber or another suitably flexible or even rigid material.
USING THE SYSTEM IN ADVERSE WEATHER CONDITIONS
In the case of particularly adverse weather conditions (e.g. strong winds) which seriously threaten the stability of the aerostat during flight, the system will be lowered and anchored securely to the ground.
In these situations, the device will continue to transmit, offering temporarily reduced radio coverage (roughly comparable to that offered by the systems used today on the Earth's surface).
As soon as weather conditions allow, the aerostat can be lifted back into the air, thus returning to greater radio coverage.
Also, during these periods of extreme weather conditions, one can take advantage of the following option: operators can capitalise on moments of calm to raise the platform and more quickly transmit data packets or make short voice broadcasts. In summary, therefore, we can absolutely say that (notwithstanding eventual time restrictions), you can transmit at greater distances than with traditional systems every single day.
USES
Here are some examples of use of the ZM-08 aerostatic platforms:
● NATURAL DISASTERS
As an example, imagine that the Civil Defence Service uses the device during an emergency, following a natural disaster.
Via the antennas installed on board, the ZM-08 aerostatic platform is able to restore radio communications for emergency crews, where ordinary connections fail, proving an excellent tool for tackling natural disasters such as earthquakes, landslides, avalanches, floods, etc.
At the same time, thanks to devices for display and aerial detection, it allows for the constant monitoring of areas affected by natural disasters and that may be subject to further earthquakes, landslides, etc.
This means greater prevention and protection of the aid staff (operating in the risk zone) and/or displaced persons located in emergency camps.
Such teams, during the course of the day, can employ the aerostat for a variety of uses. For example, the equipment mounted on the underside can be replaced temporarily or permanently to provide space for other devices: equipment suitable for weather reporting, monitoring air pollutants (generating very accurate in loco data), lighting systems, thermo-imagers, etc.
- Civil Protection
- International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement
- Fire Service
- Mountain Rescue
- Radio Aid Associations
● SAFETY AND MOUNTAIN RESCUE
In the mountain environment, the ZM-08 provide broad radio coverage by using microwaves to overcome the natural obstacles that normally hinder the efficiency of connections. At the same time, the aerial display instrumentation installed in the lower part of the aircraft the terrestrial surface may be monitored.
● SPORT
In sports, the aerostatic system is useful for radio security communications during competitions. At the same time, if the platform is arranged in an area of interest for broadcasting, it can also aerially record video to be transmitted on live TV.
The aerostat, therefore, can be used during car and motorcycle races, and in general for all competitive activities in the external environment, for example:
- Formula One
- Moto GP
- Gran Turismo
- Cart Racing
- Rally Racing
- Cycling
- Winter Sports
- Water Sports
- Other Sports
● LAW ENFORCEMENT OPERATIONS
● MILITARY OPERATIONS
● WEATHER OBSERVATIONS
● POLLUTION OBSERVATIONS
● ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH
● MEDIA/JOURNALISM
● TRAFFIC CONTROL
● VIDEO SURVEILLANCE
● TESTING/EXPERIMENTS










